Wednesday, April 30, 2014
Sunday, April 27, 2014
In electronics, a logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a boolean function that is, it performs a logical operation on one or more logical inputs, and produces a single logical output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate, one that has for instance zero rise time and unlimited fan-out, or it may refer to a non-ideal physical device.
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, boolean functions, and propositional calculus—to compute the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arguments, that is, on each combination of values taken by their logical variables (Enderton, 2001). In particular, truth tables can be used to tell whether a propositional expression is true for all legitimate input values, that is, logically valid.
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the information the schematic is intended to convey, and may add unrealistic elements that aid comprehension. For example, a subway map intended for riders may represent a subway station with a dot; the dot doesn't resemble the actual station at all but gives the viewer information without unnecessary visual clutter. A schematic diagram of a chemical process uses symbols to represent the vessels, piping, valves, pumps, and other equipment of the system, emphasizing their interconnection paths and suppressing physical details. In an electronic circuit diagram, the layout of the symbols may not resemble the layout in the physical circuit. In the schematic diagram, the symbolic elements are arranged to be more easily interpreted by the viewer.
Logic Gates and Truth Tables
| Type | Distinctive shape | Rectangular shape | Boolean algebra between A & B | Truth table | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AND | 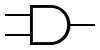 |
 |
 or or  & &  |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| OR | 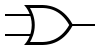 |
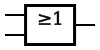 |
 |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| NOT | 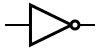 |
 |
 or ~ or ~ |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| NAND |  |
 |
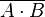 or or 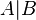 |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| NOR |  |
 |
 or or  |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| XOR | 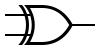 |
 |
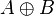 |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| XNOR | 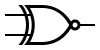 |
 |
 or or  |
| ||||||||||||||||||
The 7400 series of transistor–transistor logic integrated circuits are the most popular family of TTL integrated circuit logic. Quickly replacing diode–transistor logic, it was used to build the mini and mainframe computers of the 1960s and 1970s. Several generations of pin-compatible descendants of the original family have since become de facto standard electronic components.
References: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_7400_series_integrated_circuits
http://electronicsclub.info/74series.htm
Friday, April 25, 2014
I1
= V/R1 = 24/6 = 4 A
I2=
V/R2 = 24/12 = 2 A
I3
= V/R3 = 24/10 = 2.4 A
IT
(I1+ I2 + I3) = 4+2+2.4 = IT 8.4 A
1)
BLUE BLUE RED GOLD
66
* 100 = ± 5%
6600
* 0.5 = 3300 Ω
6600
+ 3300 = 9900 Ω
6600
– 3300 = 3300 Ω
Range
= 3300 to 9900 Ω
2)
GREEN BLUE RED SILVER
56
* 100 = ± 10%
5600
* 0.10 = 560 Ω
5600
+ 560 = 11200 Ω
5600 - 560 = 5040 Ω
Range
= 5040 to 11500 Ω
Tuesday, April 15, 2014
Series resistance is simply connecting the "out" side of one resistor to the "in" side of another in a circuit. Each additional resistor placed in a circuit adds to the total resistance of that circuit.
The formula for calculating a total of n number of resistors wired in series is:
Req = R1 + R2 + .... Rn
That is, all the series resistor values are simply added. For example, consider finding the equivalent resistance in the image below
In this example,
R1 = 100 Ω and R2 = 300Ω are wired in series. Req = 100 Ω + 300 Ω = 400 Ω
Parallel resistance is when the "in" side of 2 or more resistors are connected, and the "out" side of those resistors are connected.
The equation for combining n resistors in parallel is:
Req = 1/{(1/R1)+(1/R2)+(1/R3)..+(1/Rn)}
Here is an example, given R1 = 20 Ω, R2 = 30 Ω, and R3 = 30 Ω.
The total equivalent resistance for all 3 resistors in parallel is:
Req = 1/{(1/20)+(1/30)+(1/30)}
= 1/{(3/60)+(2/60)+(2/60)}
= 1/(7/60)=60/7 Ω = approximately 8.57 Ω.
OHMS LAW
There are certain formulas in Physics that are so powerful and so pervasive that they reach the state of popular knowledge. A student of Physics has written such formulas down so many times that they have memorized it without trying to. Certainly to the professionals in the field, such formulas are so central that they become engraved in their minds. In the field of Modern Physics, there is E = m • c2. In the field of Newtonian Mechanics, there is Fnet = m • a. In the field of Wave Mechanics, there is v = f • λ. And in the field of current electricity, there is ΔV = I • R.
The predominant equation which pervades the study of electric circuits is the equation
Schematic Symbols
| Electrical Wire | Conductor of electrical current | |
| Connected Wires | Connected crossing | |
| Not Connected Wires | Wires are not connected | |
Switch Symbols and Relay Symbols |
||
|---|---|---|
| SPST Toggle Switch | Disconnects current when open | |
| SPDT Toggle Switch | Selects between two connections | |
| Pushbutton Switch (N.O) | Momentary switch - normally open | |
| Pushbutton Switch (N.C) | Momentary switch - normally closed | |
| DIP Switch | DIP switch is used for onboard configuration | |
| SPST Relay | Relay open / close connection by an electromagnet | |
| SPDT Relay | ||
| Jumper | Close connection by jumper insertion on pins. | |
| Solder Bridge | Solder to close connection | |
Ground Symbols |
||
| Earth Ground | Used for zero potential reference and electrical shock protection. | |
| Chassis Ground | Connected to the chassis of the circuit | |
| Digital / Common Ground | ||
Resistor Symbols |
||
| Resistor (IEEE) | Resistor reduces the current flow. | |
| Resistor (IEC) | ||
| Potentiometer (IEEE) | Adjustable resistor - has 3 terminals. | |
| Potentiometer (IEC) | ||
| Variable Resistor / Rheostat (IEEE) | Adjustable resistor - has 2 terminals. | |
| Variable Resistor / Rheostat (IEC) | ||
| Trimmer Resistor | Preset resistor | |
| Thermistor | Thermal resistor - change resistance when temperature changes | |
| Photoresistor / Light dependent resistor (LDR) | Photo-resistor - change resistance with light intensity change | |
Capacitor Symbols |
||
| Capacitor | Capacitor is used to store electric charge. It acts as short circuit with AC and open circuit with DC. | |
| Capacitor | ||
| Polarized Capacitor | Electrolytic capacitor | |
| Polarized Capacitor | Electrolytic capacitor | |
| Variable Capacitor | Adjustable capacitance | |
Inductor / Coil Symbols |
||
| Inductor | Coil / solenoid that generates magnetic field | |
| Iron Core Inductor | Includes iron | |
| Variable Inductor | ||
Power Supply Symbols |
||
| Voltage Source | Generates constant voltage | |
| Current Source | Generates constant current. | |
| AC Voltage Source | AC voltage source | |
| Generator | Electrical voltage is generated by mechanical rotation of the generator | |
| Battery Cell | Generates constant voltage | |
| Battery | Generates constant voltage | |
| Controlled Voltage Source | Generates voltage as a function of voltage or current of other circuit element. | |
| Controlled Current Source | Generates current as a function of voltage or current of other circuit element. | |
Meter Symbols |
||
| Voltmeter | Measures voltage. Has very high resistance. Connected in parallel. | |
| Ammeter | Measures electric current. Has near zero resistance. Connected serially. | |
| Ohmmeter | Measures resistance | |
| Wattmeter | Measures electric power | |
Lamp / Light Bulb Symbols |
||
| Lamp / light bulb | Generates light when current flows through | |
| Lamp / light bulb | ||
| Lamp / light bulb | ||
Diode / LED Symbols |
||
| Diode | Diode allows current flow in one direction only (left to right). | |
| Zener Diode | Allows current flow in one direction, but also can flow in the reverse direction when above breakdown voltage | |
| Schottky Diode | Schottky diode is a diode with low voltage drop | |
| Varactor / Varicap Diode | Variable capacitance diode | |
| Tunnel Diode | ||
| Light Emitting Diode (LED) | LED emits light when current flows through | |
| Photodiode | Photodiode allows current flow when exposed to light | |
Transistor Symbols |
||
| NPN Bipolar Transistor | Allows current flow when high potential at base (middle) | |
|
|
PNP Bipolar Transistor | Allows current flow when low potential at base (middle) |
|
|
Darlington Transistor | Made from 2 bipolar transistors. Has total gain of the product of each gain. |
|
|
JFET-N Transistor | N-channel field effect transistor |
|
|
JFET-P Transistor | P-channel field effect transistor |
|
|
NMOS Transistor | N-channel MOSFET transistor |
|
|
PMOS Transistor | P-channel MOSFET transistor |
Misc. Symbols |
||
|
|
Motor | Electric motor |
|
|
Transformer | Change AC voltage from high to low or low to high. |
|
|
Electric bell | Rings when activated |
|
|
Buzzer | Produce buzzing sound |
|
|
Fuse | The fuse disconnects when current above threshold. Used to protect circuit from high currents. |
|
|
Fuse | |
|
|
Bus | Contains several wires. Usually for data / address. |
|
|
Bus | |
|
|
Bus | |
|
|
Optocoupler / Opto-isolator | Optocoupler isolates connection to other board |
|
|
Loudspeaker | Converts electrical signal to sound waves |
|
|
Microphone | Converts sound waves to electrical signal |
| Operational Amplifier | Amplify input signal | |
|
|
Schmitt Trigger | Operates with hysteresis to reduce noise. |
| Analog-to-digital converter (ADC) | Converts analog signal to digital numbers | |
| Digital-to-Analog converter (DAC) | Converts digital numbers to analog signal | |
| Crystal Oscillator | Used to generate precise frequency clock signal | |
Antenna Symbols | ||
| Antenna / aerial | Transmits & receives radio waves | |
| Antenna / aerial | ||
| Dipole Antenna | Two wires simple antenna | |
Logic Gates Symbols |
||
| NOT Gate (Inverter) | Outputs 1 when input is 0 | |
| AND Gate | Outputs 1 when both inputs are 1. | |
| NAND Gate | Outputs 0 when both inputs are 1. (NOT + AND) | |
| OR Gate | Outputs 1 when any input is 1. | |
| NOR Gate | Outputs 0 when any input is 1. (NOT + OR) | |
| XOR Gate | Outputs 1 when inputs are different. (Exclusive OR) | |
| D Flip-Flop | Stores one bit of data | |
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)








